Polymers, as macromolecules, are made up of small monomer units that are linked together to form longer, more complex structures. These multifaceted and complex materials are the result of various processes, including synthetic synthesis, that have been developed throughout history.
Polymers are present all around us in various forms and play a very important role in different societies. From the chain structure of DNA to materials such as polypropylene, these materials are used in a variety of industries and applications. Polymers can be found naturally from biological sources or produced through synthetic processes.
With a variety of physical and chemical properties, polymers are exploited as the most important materials in the production of products and services in different industries and play a very important role in our daily lives. In this article, we will take a broader look at polymers and their various applications in a variety of industries and societies.
Introduction to polymers
Polymers are a class of materials that are made up of very large molecules called macromolecules. These macromolecules are made up of smaller units, or monomers. In fact, polymers are made up of small molecules called monomers. These connections between monomers form long chains, also called backbones, through chemical bonds.
The word “polymer” comes from two Greek words, poly and mer, which mean “many” and “parts,” respectively. In polymers, monomers are linked together in large numbers to form long structures.
What is a monomer?
A monomer is the smallest repeating unit of a polymer. In other words, these molecules are the building blocks of polymers. For example, if you think of a rosary as a polymer chain, each bead of the rosary acts as a monomer in this chain. Each bead is a repeatable, basic unit that is repeated in the polymer structure.
Various properties of polymers
As mentioned, polymers are derived as compounds from smaller units called monomers, and these bonds are created through chemical reactions. These compounds are divided into two main categories: natural polymers and synthetic polymers.
In natural polymers, such as wood, natural rubber, and resin, the polymer structure is created from natural molecules found in the environment. On the other hand, synthetic polymers, such as plastics, nylons, and glass, are produced by humans using industrial processes. These polymers are divided into two categories: thermoplastics and thermosets based on their reactivity to heat.
Thermoplastics, or thermoplastics, melt when heated and can be reshaped. In contrast, thermosets, or thermosets, have a higher melting point and do not melt when heated. This classification is influential in the production of polymer products and their processing.
Types of polymers in terms of physical properties and applications
Plastic
Polymers that are transformed into hard and rigid materials under the influence of heat and pressure.
They are usually semi-crystalline and their intermolecular properties lie between fibers and rubber.
Examples: PMMA, PE and …


2
Rubber or elastomer
Solid polymers with high elasticity properties, in which the polymer chains are connected by the weakest intermolecular forces.
Most of their structure is amorphous, and these weak intermolecular forces cause their high elasticity.
Example: Rubbers and …
Fibers
Long filamentous polymers whose length is at least 100 times their diameter.
They have very high tensile properties and a high degree of crystallinity.
Example: Nylon and …

Resins
Low molecular weight polymers used as adhesives, sealants, etc.
They are often in liquid form and are usually cured after or after application to increase their strength.
Example: Air-curing adhesives usually cure and harden after exposure to air for a period of time.
Commonly used polymers:
Common polymers will be described below;
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene (PE) is one of the most important and widely used polymers used in a variety of materials and equipment. This polymer is composed of 2 carbon atoms and 4 hydrogen atoms and has different forms depending on the configuration of its molecular chain. Based on the arrangement of ethylene molecules, it is also called a homopolymer.
-
Advantages of polyethylene
- Availability and low cost, it is used in many industries and applications.
- Electrical insulation: This polymer acts as a good electrical insulator, which makes it widely used in the electronics industry.
- Resistance to solvents and dilute acids: Polyethylene is well resistant to It is resistant to solvents and dilute acids.
- Resistance to tearing: This feature has made it a widely used material for packaging and similar uses.
- Transparent models: This polymer is also produced in transparent forms that are used in the bottling and food packaging industry.
Polyethylene applications
- Water and soft drink bottles
- Food packaging and Food
- Plastics for shopping
- Pipe and fittings
- Stretch film and shrink film
- Medical implants
- Clothing types
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic additive polymer made from a combination of propylene monomers. With unique chemical and physical properties, this polymer is used in various industries and everyday life.
Properties of Polypropylene
- High flexibility and strength: Polypropylene is used in packaging and various equipment due to its flexibility and high impact resistance.
- Electrical insulation: This polymer is also known as an electrical insulator, which is used in the electronics industry.
- Variety in opaque and transparent surfaces: Polypropylene can create opaque or transparent surfaces, which increases the variety of its applications.
- Resistance to tearing and puncture: High resistance to tearing and puncture makes this polymer a suitable material for packaging.
- Chemical resistance: Polypropylene is resistant to corrosion and the effects of various chemicals.
Applications of Polypropylene
- Food packaging and equipment: This polymer is used in the packaging of food products due to its food resistance and corrosion resistance.
- Medical products: Including syringes, pill containers, or sampling containers Made from polypropylene.
- Detergents and bleaches: This polymer is used in the production of detergents and bleaches as packaging or containers.
Polypropylene, as a widely used material in various industries, helps to improve the efficiency and application of various products due to its unique properties.
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), also known as PETE, is a type of polyethylene that is widely used in everyday life. With a melting point of 260 degrees Celsius, PET is durable in high-temperature environments. This lightweight, strong, and transparent polymer is used in the food and beverage packaging industry.
PET is made up of two main elements, ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid, which are linked together to form a polymer chain.
Features of polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
- High strength and hardness: PET is used in packaging various materials due to its high strength and hardness.
- Lightweight: This material is used as a lightweight polymer in the production of bottles and transparent packaging.
- Electrical insulation: PET is also used as an electrical insulator.
- Low gas permeability: The low gas permeability property makes this polymer suitable for packaging materials. Oxygen sensitive.
- Suitable for transparent packaging: This feature makes PET popular in transparent packaging.
- Tear resistance: PET‘s tear resistance makes it a suitable choice for packaging a variety of products.
Applications of PET
- Plastic sauce bottles
- Oil packaging
- Glass bottles Clear for shampoo and liquid soap
- Packaging for cleaning and bleaching products
Polyamide or nylons (PA)
Polyamides are a group of synthetic polymers that are made up of different types of polymers. They have moderate moisture absorption and relatively low heat retention, and are rich in hydrogen bonds. These bonds increase the crystalline properties, chemical resistance, and heat resistance of the material. Polyamide is used in materials such as wool, silk, collagen, and keratin.
Main properties of polyamides
- Low resistance to moisture: Polyamides are somewhat sensitive to moisture.
- High impact resistance: These polymers have high impact resistance due to their molecular structure.
- High tensile strength: Polyamides, unlike many polymers, have high tensile strength.
Main applications of poly Amides
- Textile and textile industry: for the production of durable and high-quality fabrics.
- Production of silk, wool carpets, etc.
- Manufacturing of kitchen utensils: due to their resistance to impact and heat.
- Sportswear and bulletproof vests: for increased strength and resistance to damage.
- Automotive industry: for use in various parts, including pipes.

Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), also known as PETE, is a type of polyethylene that is widely used in everyday life. With a melting point of 260 degrees Celsius, PET is durable in high-temperature environments. This lightweight, strong, and transparent polymer is used in the food and beverage packaging industry.
PET is made up of two main elements, ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid, which are linked together to form a polymer chain.
Features of polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
- High strength and hardness: PET is used in packaging various materials due to its high strength and hardness.
- Lightweight: This material is used as a lightweight polymer in the production of bottles and transparent packaging.
- Electrical insulation: PET is also used as an electrical insulator.
- Low gas permeability: The low gas permeability property makes this polymer suitable for packaging materials. Oxygen sensitive.
- Suitable for transparent packaging: This feature makes PET popular in transparent packaging.
- Tear resistance: PET‘s tear resistance makes it a suitable choice for packaging a variety of products.
Applications of PET
- Plastic sauce bottles
- Oil packaging
- Glass bottles Clear for shampoo and liquid soap
- Packaging for cleaning and bleaching products
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is one of the most important polymers in the world, playing a key role in the production of many plastic equipment. The production process of this material includes the extraction of salt and hydrocarbon resources, the production of chlorine and ethylene, the combination of chlorine and ethylene to produce vinyl chloride monomer, the polymerization process to produce polyvinyl chloride, and the combination of PVC polymer with other materials to create various compounds.

Main Features of Polyvinyl Chloride
- Long life and high resistance: PVC has a long life and high resistance to impact and scratches.
- High density and density: It offers a large amount of polymer in specific weight and unit volume.
- Economical: The production process of this polymer is carried out economically.
- High hardness: PVC has a hard surface and is resistant to scratches.
Main uses of polyvinyl chloride
- Construction and civil engineering: Widely used in pipes, windows and flooring.
- Medical equipment: For the production of pipes and medical devices.
- Electrical and electronics industry: In the production of cables and electronic components.
- Automotive industry: For the production of interior and exterior parts of cars.
- Pipes and fittings: Due to their corrosion resistance in water and sewage systems.
- Wire and Cable: In the production of electrical wires and cables.
- Packaging Film: For the production of flexible films for packaging.
Polystyrenes (PS)
Polystyrene (PS) is a thermoplastic polymer made from styrene monomers. It is reusable due to its melting and heating properties. In addition, PS is an excellent electrical insulator and has high resistance to chemicals such as acids and bases.
One of the important examples of the use of PS is ABS plastic (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene), which is produced by the simultaneous polymerization of styrene, acrylonitrile and butadiene. This combination improves the properties and applications of polystyrene.
Applications of Polystyrene
- Medical equipment: It is used in the manufacture of medical equipment parts as a material with desirable properties.
- Use as an insulator: As an excellent electrical insulator in various industries.
- Resistant food packaging: In the production of containers and packaging used in the food industry.
- Plastic kitchen utensils: Manufacture of household appliances and utensils used in the kitchen.
Polycarbonates (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) refers to a class of polymers that contain carbonate groups in their structure. Due to its high flexibility, this polymer can be modified or corrected at ambient temperature without causing breakage in its molecular structure.

Polycarbonate Features
The following are some of the features of polycarbonate:- High strength and hardness in engineering industries.
- Has two types: opaque and completely transparent.
- Easy to use and obtain.
- Suitable flexibility.
Polycarbonate Applications
- Eyewear manufacturing: As a durable and lightweight alternative to regular glasses.
- Medical devices: Used in medical equipment due to its good stability.
- Protective equipment: Such as helmets are produced using polycarbonate.
- Automatic devices: For the manufacture of automatic parts and devices.
- Lighting and lighting equipment: Due to its transparency, it is used in the manufacture of lamp components and lighting equipment.
Masterbatch review and its special applications
As mentioned, polymers are divided into two basic categories as materials that are made up of smaller units called monomers and are linked together through chemical reactions. These two categories of polymers include natural polymers and synthetic polymers.
Masterbatch is a concentrated mixture of three main elements: the base polymer, additives, and a compatibilizer. The base polymer is usually made of ethylene vinyl acetate, polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene or other special polymers and should be similar to the plastic used in plastic injection molding. By adding additives to the base polymer, the mechanical and appearance properties of the polymer are improved. These additives can include pigments, special improvers, and fillers. A compatibilizer is also used to increase the compatibility of the additives with the base polymer. Masterbatches have a variety of applications. For example, additive masterbatches are widely used in the production of medical devices. In the production of syringes, additives reduce friction and increase slip. Also, in the production of polymer films, anti-blocking masterbatches reduce the adhesion of film surfaces. Different types of masterbatches include color, additive, and filler masterbatches. Antistatic masterbatches are used to prevent dust from being absorbed on the surface of products. Also, masterbatches containing antioxidants are used to increase the strength and stability of polymer materials. Masterbatches are effective solutions in improving the properties of polymers and creating special features in final products.Thermoplastics, also known as thermoplastics, melt in the presence of heat and can be deformed and recycled many times. In contrast, thermosets, also known as thermosets, have a higher melting point and do not melt when exposed to heat. This classification helps to distinguish polymers and their thermal properties, and is influential in the production of polymer products and their processing.

Examining some polymer applications
Polymer in the packaging industry
The packaging industry has experienced major changes in various industries, especially the food industry, by using polymer materials extensively. Replacing polyethylene bottles with metal containers and packaging chemicals such as acids and toxins with these materials has not only helped improve hygiene but also reduced costs.
The use of polymers in food packaging, including soft drinks and oils, has attracted attention due to the protective and protective properties of these materials. Also, the manufacture of various plastic bottles and caps has facilitated the use and transportation of products, and as a result, has brought prosperity and increased consumption in these industries. These developments have not only helped to improve public health, but also contributed to the economic development of these industries by reducing costs.
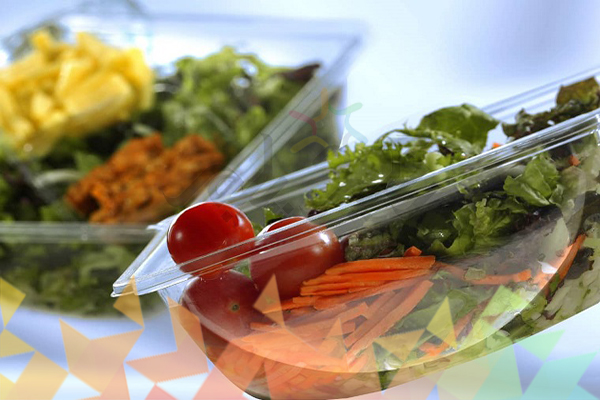
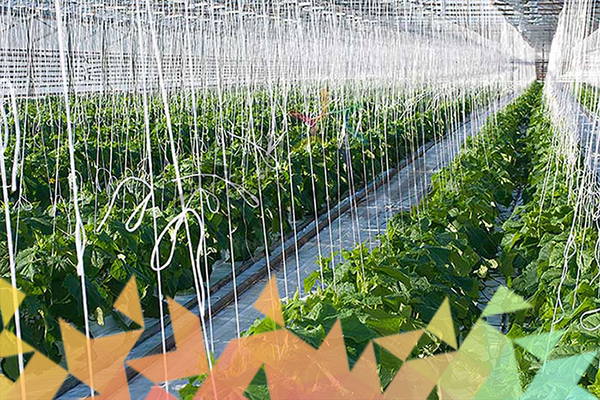


Polymer in the agricultural industry
The increasing use of polymer materials in the agricultural industry plays a significant role in the development of this field. Optimization of water consumption is one of the most important advantages of using polymer products in agriculture. The polyethylene pipes and films that are used have not only helped to significantly reduce water waste, but also revolutionized this industry by becoming a means of exploiting crops in water-scarce areas.
The use of these pipes and films allows farmers to harvest a variety of crops with advanced methods in areas that were previously unsuitable for agriculture. These innovations have not only helped to improve productivity in agriculture, but have also contributed to more sustainable management of water resources and increased agricultural production on a large scale.
Polymers in the construction industry
Polymers have brought about significant changes as a key component in the construction industry. These materials not only give buildings a beautiful and diverse appearance but also solve the problems associated with traditional materials. Since polymers can be used in most stages of construction, these materials are used in modern buildings.
The use of polymers in buildings includes thermal and moisture insulation, plastic pipes, windows and various other components. These materials have responded to the problems of heat transfer, insulation, and the construction of lightweight and weather-resistant structures as efficient and high-performance alternatives. These developments also help to increase energy efficiency and reduce construction costs.

Choosing quality and colorful polymers for industrial applications
Polymers are a broad and vital class of materials used in materials science and chemistry. These compounds are chains of repeating molecules that have many properties and applications in various industries. From plastics with flexibility and lightness to rubbers with high elasticity and fibers with strong tensile strength, various types of polymers differ in terms of structure, behavior against heat, and physical properties.
Tactical arrangement, crystalline arrangement, and their origin are among the different characteristics that have a great impact on the behavior and application of these polymers. This diversity and flexibility have made polymers a unique tool in the production of various materials and products and have played a very important role in the advancement of industry and technology, especially in recent decades.
In order to select the types of polymers required in their industrial activities, Rangin Polymer Group is ready to provide advice to our valued customers.

Frequently Asked Questions
Polymers are a class of materials that are made up of large molecules called macromolecules. These macromolecules are made up of smaller units, or monomers, and are linked together by chemical bonds.
- Long formation: Long chain molecules called backbones.
- Multiplicity: Different types of polymers are made from different monomers.
- Order or disorder in structure: The structure of polymers may be naturally ordered or disordered.
- Polyethylene (PE): Used in packaging, pipes, electrical appliances and many other products.
- Polypropylene (PP): Used in packaging, pipes, furniture and various industries.
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): Used in pipes, flooring, clothing and other products.
Polymers can be recycled, and the process can involve collecting, grinding, remelting, and manufacturing new products. This has a positive impact on the environment and increases the reuse of finite resources.




